Programming in Python
1 Install Python
You can skip this section if you are using a lab computer with Python already installed. Otherwise, download Python 3 from the Python web site. The install process is entirely straightforward, just work your way through the steps.
2 Start your program
- From the Windows Start menu, select All Programs » Python 3.x »
IDLE. There will be a similarly named program in Applications »
Python 3.x on the Mac.
- A window called the “Python Shell” will appear. It displays a
prompt like
>>>. This is the window in which you will interact with your program.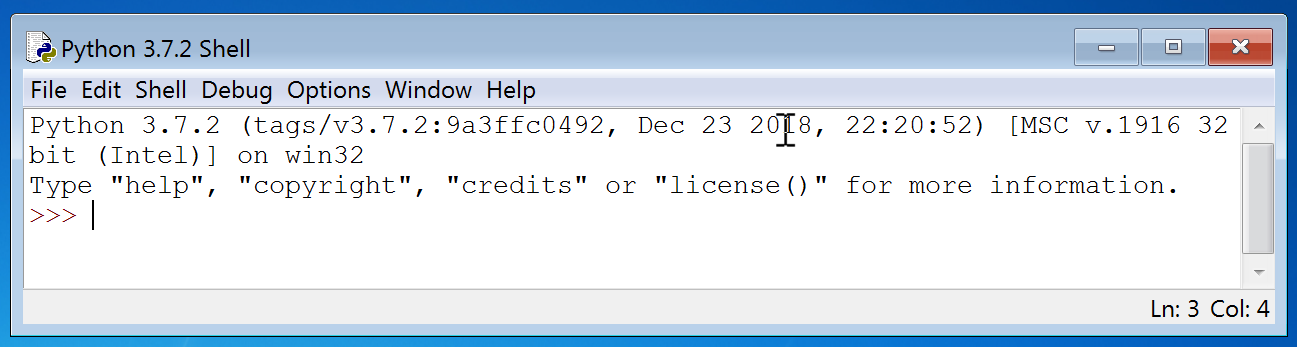
- You need a second window, in which you will type and save the
content of your program. Select File » New File from the menu.
- While in the new window, select File » Save and give it a
filename that ends with
.py(this will enable syntax coloring). You can also choose the folder to save it in, such as your Documents or Desktop folder.
- Type your code into the
.pyfile, and save it with File » Save, or Ctrl-S or ⌘-S. - Use Run » Run Module (F5) to run it, and interact with the program
in the Shell window.
3 Printing messages
Here is a program you can try that prints messages on the screen. You
can copy and paste this block into your .py file, then save and run.
(Note: the coloring used on this web page may not precisely match the
colors you see in IDLE.)
print("Hello!") print(3+4) print("3+4") print("2*7 is", 2*7)
When you run this program, the Shell window will contain:
>>> ====================== RESTART ====================== >>> Hello! 7 3+4 2*7 is 14 >>>
The double quotes indicate a string of characters (text). That portion
is output exactly as written. Any portion not in quotes is interpreted
by Python. Thus the difference between printing 3+4 (which produces
7) and printing "3+4".
4 Fixing errors
The most common error you will see is probably “Invalid syntax”. It pops up like this:
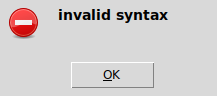
Dismiss that message, and you see it also highlights a portion of your program in red.
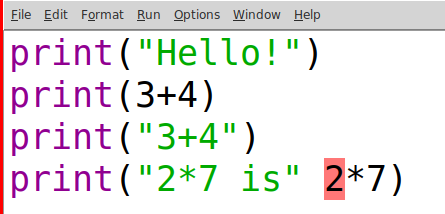
Often the red part is just after the source of the actual error. In this case, we omitted the comma between the two different things in the print statement on that line.
Another kind of error shows up in the Shell window. It might look like this:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/Users/league/Desktop/myprogram.py", line 4, in <module>
print("2*7 is", x)
NameError: name 'x' is not defined
The actual error is the last line. This one is called a NameError. But
the Traceback section can help you too, by telling you which line
number to examine (in this case, line 4).
5 Doing calculations
We can store variables very simply in Python by using an equals sign. Variable names consist of a sequence of letters, numbers, and underscores (no spaces), but they cannot start with a number. Here are examples of valid variable names:
quiz3the_last_dayFrankx
These are not valid:
quiz 32nd_quiz
Variable names are case-sensitive, so x and X are both valid, but
they are not the same variable. Below is a program that uses variables
to perform a computation.
quiz1 = 32 quiz2 = 40 quiz3 = 16 average = (quiz1 + quiz2 + quiz3) / 3.0 print("Average is", average)
When you run it, the output should look something like this:
>>> ====================== RESTART ====================== >>> Average is 29.333333333333332
Python (and most languages) distinguish between numbers that are
integers (whole numbers), and numbers that can contain decimal points.
The latter are called floating-point numbers. When you divide two
integers, Python 3 automatically converts them to floating-point – not
every language does this. If you want integer division, use a
double-slash (//) as the divide operator.
>>> 9/2 4.5 >>> 3/4 0.75 >>> 9//2 4 >>> 3//4 0
6 Comments
It is often useful to add notes to your program, for yourself or other
humans. Any text on a line that follows a pound sign (#) will be
ignored by Python. So we can use this facility to add a header
describing the program:
# quizzes.py -- This program calculates quiz scores # by Christopher League print("Welcome to the quiz calculator!")
Or to explain a particular piece of code on the same line:
average = (quiz1 + quiz2 + quiz3) / 3.0 # Add first, then divide
It can even be used to disable a line of code without deleting it from your program… then it’s easy to put back if you need to. This is called “commenting out” code.
total = quiz1 + quiz2 + quiz3 #print(total) average = total / 3.0 print(average)
7 Getting input
Python has a very handy built-in function for receiving input from the user of your program. It works like this:
name = input("Enter your name: ")
On the left side of the equal sign is a variable name. On the right side
is the input function. In the parentheses, you specify a string that
will be the prompt presented to the user. When you run the above
program, it looks like this:
>>> ====================== RESTART ====================== >>> Enter your name:
You are expected to type something at this point, and press enter.
Whatever string you type will be placed into the variable name. Here’s
a more complete sample program:
name = input("Enter your name: ") print("Welcome to my program,", name) year = int(input("What year were you born? ")) age = 2019 - year print("You are", age, "years old.")
Running the program looks like the following. The parts the user types are indicated by «angle quotes».
>>> ====================== RESTART ====================== >>> Enter your name: «Chris» Welcome to my program, Chris What year were you born? «1988» You are 31 years old.
8 Boolean expressions
Python has values for Booleans – they are called True and False.
Note that, like variable names, they are case-sensitive, so you must
capitalize them as shown. There are also operators that produce
Boolean values. The most obvious ones are for numeric comparisons.
Consider this transcript in the Python shell:
>>> 3 < 5 True >>> 3 > 5 False >>> 2 < 2 False >>> 2 <= 2 True
The last example in that block is <=, pronounced “less than or equal.”
There is also >= for “greater than or equal.” You cannot have a space
between the two operators: < = will be a syntax error.
Checking whether two things are exactly the same is a little tricky. The
equals sign = is already used to mean variable assignment, as in:
my_quiz_score = 38
This statement above does not ask whether my_quiz_score is equal
to the value 38. Instead, it sets the value of that variable to 38,
and whatever value it had previously is lost.
In order to ask the question, whether a variable is equal to a certain
value, you need to use a double equal sign: ==, like this:
>>> my_quiz_score == 38 True >>> 38 == my_quiz_score True >>> 21 == my_quiz_score False >>> 19 == 19 True >>> 19 == 21 False >>> "nice" == "evil" False >>> "nice" == "nice" True
The opposite of the equality operator is !=, and it is simply
pronounced “not equals.”
>>> my_quiz_score != 38 False >>> 38 != my_quiz_score False >>> 21 != my_quiz_score True >>> 19 != 19 False >>> 19 != 21 True >>> "nice" != "evil" True >>> "nice" != "nice" False
9 Compound Booleans
Python also has operators from Boolean logic; they are called and,
or, not. Here are a few examples involving them:
>>> 3 > 5 or 5 < 6 # becomes False or True, which is True True >>> 3 > 5 and 5 < 6 # becomes False and True, which is False False >>> not True False >>> not (3 > 5) True >>> my_quiz_score >= 0 and my_quiz_score <= 40 True
That last example determines whether the value of my_quiz_score is
within a certain range: from zero to forty, inclusive.
10 Conditional statement
Now that we’ve seen Boolean expressions, we’re ready to explore
conditional statements. They have a keyword if (must be lower case),
and then the Boolean expression, followed by a colon (:) – it’s a
very common mistake to forget the colon!
On the next line, and indented a few spaces, you put any statements that should be executed only if the condition is true. Here is an example:
if my_quiz_score > 32: print("Congratulations, that's a good score.") grade = "A" print("Thanks for taking the course.")
You can see that the last print statement in that block is not
indented. That means it is no longer controlled by the if. If we reach
this code when the value of my_quiz_score is 38, the output will be:
Congratulations, that's a good score. Thanks for taking the course.
And the variable grade will contain the text string "A". On the
other hand, if my_quiz_score is 31, the output will be only the last
line:
Thanks for taking the course.
It’s also possible to provide an else block that executes when the
if block doesn’t. Here’s a complete program you can paste into the
Python program window and run with F5:
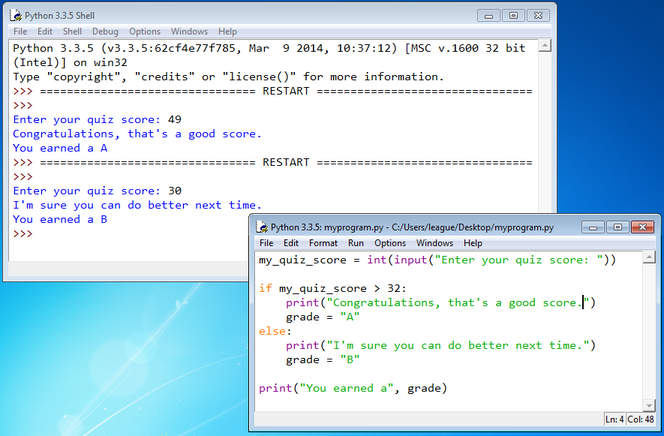
my_quiz_score = int(input("Enter your quiz score: ")) if my_quiz_score > 32: print("Congratulations, that's a good score.") grade = "A" else: print("I'm sure you can do better next time.") grade = "B" print("You earned a", grade)
When you run it, try entering different values at the prompt in the shell window, and observe the results.
11 If/else chain
It’s a fairly common pattern to “chain together” a series of if/else conditions, something like this:
if my_quiz_score > 32: grade = "A" else: if my_quiz_score > 24: grade = "B" else: if my_quiz_score > 16: grade = "C" else: grade = "D"
You can see that the indentation increases each time an if is embedded
within the else of another if. Try tracing this code with
my_quiz_score set to different values, to see what ends up being
stored in grade. You may even want to revise the previous program
using this technique, so it can output more than just A or B.
This chain is common enough that Python provides a shortcut for it so
that the continued indentation doesn’t get out of hand. The shortcut
relies on the keyword elif, and it looks like this:
if my_quiz_score > 32: grade = "A" elif my_quiz_score > 24: grade = "B" elif my_quiz_score > 16: grade = "C" else: grade = "D"
This program does the same thing as the previous one, but it’s a little cleaner and shorter.
12 Exercises
These are helpful exercises, to test putting it all together. First, create a program that does the following:
Enter quiz 1 score: «90» Enter quiz 2 score: «80» Your average is 85.0 Your grade is B
It can just use 90/80/70/60 as the thresholds for A/B/C/D. Once you have that working, try this one:
Enter quiz 1 score: «60» Enter quiz 2 score: «95» Enter quiz 3 score: «92» Dropping the 60 Your average is 93.5 Your grade is A
It will ask for three scores, but then drop the lowest one before computing the average of the other two.
13 Reopening your programs
Once you have saved your .py file, it may not work just to
double-click your file again to reopen it. That will run the program
in a console window, which is especially awkward because it might not
pause to show the output before the window disappears.
Instead, you can right-click in the .py file and select “Edit with
IDLE” (if on Windows). Or simply open IDLE first and then use the File
» Open menu and navigate to the .py file from there.
14 Other sample programs
Calculate wage and taxes
wage = float(input('Enter your wage: ')) hours = int(input('How many hours: ')) pay = wage * hours if pay > 10000: print("You owe 10% in taxes.") pay = pay * 0.9 print("Your pay is $", pay)
A loop to calculate a sum
answer = 0 counter = 1 # Count from 1 to 100 while counter <= 100: print(counter) answer = answer + counter counter = counter + 1 print("The sum is", answer)
Repeat a fixed number of times
This prints a bunch of powers of two using a for loop.
count = 1 print(count) for i in range(200): count = count*2 print(count)
Repeat based on condition
This is a variation of the previous, where we find the first power of two that is larger than ten million.
count = 1 while count <= 10000000: count = count * 2 print(count)
Factorial calculation
n = int(input("Enter an integer >0: ")) k = 1 while n > 1: k = k * n n = n - 1 print(k)
Euclid’s greatest common divisor
a = int(input("Enter an integer >0: ")) b = int(input("Enter another integer >0: ")) while a != b: if a < b: b = b - a else: a = a - b print(a)
Simulate coin flips
import random numFlips = 10000000 numHeads = 0 for i in range(numFlips): secretNumber = random.randrange(1,101) if secretNumber > 50: coinflip = "HEADS" numHeads = numHeads + 1 else: coinflip = "TAILS" #print(coinflip) percent = (numHeads / numFlips) * 100 print("There were", numHeads, "heads:", percent, "%")